Frequently Asked Questions
Many pages on this site feature FAQs – here are all the FAQs together in one place.
What do I do first?
The best place to start is with thinking about what you want, understanding your goals and concerns, and looking at other ADUs for inspiration. Once you have some ideas in mind, you can consider your budget and move on to Learning the Rules to figure out what you can build on your property.
You can also use your County Process-at-a-Glance resource for an overview of the steps and some initial issues to consider as you get started.
Are there specific guidelines about fire safety?
If your property is in a Fire Hazard Severity Zone or Fire Protection District there may be additional requirements or reviews. Find out about your location and talk to staff early on to learn how where you live might impact your ADU. Use the Fire Hazard Severity Zone Tool to look up your property and identify your zone and see our Resources page for more information.
Can an ADU or JADU be used as a short-term/vacation rental?
No. Generally, J/ADUs are not allowed to be rented for less than 30 days. This discourages the listing of ADUs on popular websites like Airbnb and VRBO and promotes them as a means to increase housing stock for the diverse needs of county residents. You may be required to file a deed restriction agreeing that the unit will not be used for short-term rentals.
What do I need to know about becoming a landlord?
Renting an ADU comes with many responsibilities, including understanding local and state housing laws, executing a lease, finding and managing a tenant, and maintaining a rental property. It’s important to understand the laws as they may affect things like future rent increases, changing use over time, evicting tenants, and moving family into the unit.
See your County Guidebook for resources on understanding rental laws, tenants’ rights, and more, and Exercises for help with your lease terms.
When is my ADU ready for move-in?
As soon as the final inspection is complete, your ADU is ready for move-in! Make sure utility services are set up, an address is established, and other preparations are in place. See below for more responsibilities of being a landlord.
What are my responsibilities during construction?
While your contractor will lead the construction process, you will have the following responsibilities:
- Keep in touch with your contractor and set up a schedule for checking in.
- Regularly walk through the construction area to monitor the quality of the work and make sure the work is progressing the way you expect.
- Be prepared to make decisions about the details—light fixtures, appliances, and other materials—in a timely manner so your contractor can stay on schedule.
- Follow the contract you agreed to, including any changes as described specifically in a change order form.
- Although your contractor will usually arrange the required county or utility inspections, it is your responsibility as the property owner to make sure that the inspections are conducted as required.
How long does construction take?
Traditional construction will take 6-12 months, though this will vary depending on the specifics of the project. Stages of construction include:
- Site preparation: 1-2 months
- Foundation: 1 month
- Walls, roof, doors: 1-2 months
- Plumbing & electrical: 1-2 months
- Insulation & drywall: ½-1 month
- Fixtures & finishes: 1-2 months
- Final touches: ½-2 months
How can I keep construction costs down?
Construction costs for your ADU will vary significantly depending on personal preferences, site conditions, location, and many other factors.
Size: Despite what many think, smaller ADUs may cost almost the same as larger ones. Many costs like foundation, kitchen and bathroom work only increase slightly for larger ADUs. Kitchen costs will range from $25,000–$50,000 with each bathroom ranging from $15,000–$25,000.
Type: New construction, both detached and attached, tend to be the most expensive. Garage conversions are not much cheaper than new construction if at all. Conversions of interior space (basement or otherwise) are often the cheapest.
Other factors:
- Quality of interior finish work and amenities
- Architectural form and details
- Extent of utility, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing upgrades required
- Required site upgrades (sidewalks, sewer and water)
- Whether sprinklers are required
- Whether doors and windows meet emergency exit standards
- Lot complexity (slope, trees, fault lines, etc.)
How do I find a contractor?
If you are not using a design/build firm, you will need to find a contractor to take over for the construction phase of your ADU.
First, you’ll solicit bids. See your County Guidebook for more details on what you want to see in a bid, what other documentation to collect from potential contractors, and what to look for in your bidding candidates. You will want to get at least three bids for comparison.
When you have bids, you can begin selecting your contractor. See the Guidebook for more details on how to compare bids and choose the best option for you.
Before you hire a contractor, make sure to check their license and insurance and when they present you with a contract, review everything carefully. See the Guidebook for more details.
What if I have an unpermitted ADU?
State law says an ADU permit cannot be denied due to nonconforming zoning, building code violations or unpermitted structures unless there is a threat to public health or safety, and they are not affected by building the ADU.
Existing unpermitted ADUs can go through the permitting and approval process set out in your County Guidebook. Planning staff will work with you to determine what would be involved to bring your ADU up to code. To note, if you constructed your ADU within the last ten years, you will be required to submit an engineer’s report and a Title 24 Energy Report.
For unpermitted ADUs built before January 1, 2018, state law says a permit to legalize cannot be denied even if there is a violation of ADU laws or building standards, unless it is a “health and safety concern” or if the building is deemed “substandard” by state Health and Safety Code.
Can my ADU be stopped because of other noncompliance issues on my property?
In most cases, state law no longer allows cities and counties to comment on pre-existing zoning issues unrelated to the ADU. For example, you should not receive comments about correcting the main house or a fence unrelated to the ADU, unless there is an obvious public safety issue.
Are there water or sewer issues I should consider?
If you are connected to a municipal sewer system you may be required to upsize service and or meters to meet capacity requirements. Check County ADU Rules and talk with staff to learn more about local requirements for sewer connections. ADUs on properties with septic often need separate waste treatment and your existing system may need to be modified. Wells also may need special permits and review. Contact your Environmental Health Department early in the process. For contact information, see the Contact page.
What permits are required for ADUs and JADUs?
Submitting an application is different in each county. Some have online portals while others ask for multiple sets of paper copies on various sizes of paper. Some may require one application package, while others require separate review by the Planning and Building departments. Check with local staff to confirm the application process and requirements and for details about permit materials.
Does the county have available ADU plans?
The Mother Lode ADU Plans Gallery provides property owners interested in building an ADU with an easy way to compare and select from dozens of plans – including modular/prefab and site built – saving you both time and money. Like many online shopping experiences, you can filter by the kind of ADU you want (number of bedrooms, square footage, features) then view photos, floorplans, and details of all the designs you like. You can then connect directly with the designer or company.
When do I show the County my designs?
Once you have a design established with your architect/designer, it’s a great idea to discuss it with County staff so they can point out any issues before you prepare your application.
You may be able to schedule an appointment to speak with a planner or walk in to the Planning Counter or Permit Center. For contact information, see Contact page.
This is also a good time to reach out to utility agencies (water, sewer, gas, etc.) to inquire about their infrastructural requirements and confirm connection and service fees.
How do I find an architect or designer?
Most homeowners choose to work with some type of design professional to plan their ADU and help throughout the process. Bringing on a professional early in the process is often key to getting your ADU approved quickly, managed efficiently, and built cost-effectively. Relevant experience and fit will be critical.
There are a variety of types of designer, and they may be an architect, builder, “designer,” design/build, or a modular/prefab company. If you’re hiring a local individual or team, they’ll likely start the process by visiting your home and talking to you about your ideas and goals. If it seems like a good match, they will prepare a proposal detailing their services and fee. Professionals typically charge for an initial consultation or proposal.
Note that if you’re not using a licensed architect to design your ADU, your plans may need to be stamped by a licensed engineer. Check with your staff early on.
See the Exercises for a list of questions to ask a potential architect or designer, the Glossary to be clear on terms, and your County Guidebook for more details.
What about the money I could make renting the ADU?
Rental income is a major benefit of having an ADU or JADU on your property – for many people, it provides flexibility in their budget or an opportunity to grow their savings. Generally, you cannot rent your ADU for less than 30 days at a time (e.g., AirBnB, Vrbo). The County ADU Calculators can help you estimate how much rental income could be generated by your new unit.
Can I eventually sell my ADU separately from the main building?
Usually not and you may need to record in a deed restriction for the property that the ADU cannot be sold separately from the primary home. Check County ADU Rules to find out what local restrictions apply.
How will building an ADU affect my taxes and property value?
Adding an ADU will likely affect your property taxes and the resale value of your home. However, your primary house will not be reassessed, and your property taxes will only increase based on the added value of your ADU. For example, if you build an ADU that adds $150,000 to your property value, and your tax rate is 1%, your taxes will increase by 1% x $150,000, or $1,500 per year.
Building a JADU will have a significantly smaller impact on assessed value. In some cases, your taxes will not increase at all. Home sharing will also not increase the assessed value of your home. Generally, garage conversions will not raise your tax bill as much as new construction, but they will also not add as much value.
Each property will require a one-on-one analysis to determine the added value of an ADU, so contact your County Assessor’s Office once you have an idea of your plan. They may be able to provide you with a rough estimate of tax implications.
Adding an ADU may impact your income taxes as well. This can be rather complicated, and it’s best to discuss these with a tax advisor.
What if I don’t have a lot of money available right now to build an ADU?
If you have equity in your home, a cash-out refinance or home equity loan/line of credit (HELOC) might work for you. Financing is typically unavailable for homeowners with lower income and insufficient home equity. The California Housing Finance Agency (CalHFA) ADU Program provides a grant of up to $40,000 to qualified homeowners for the reimbursement of ADU pre-development costs, including but not limited to impact fees. To qualify, a homeowner must be low or moderate income. Make sure to check if funds are available and if you qualify.
How am I going to pay for an ADU?
Many homeowners use a mix of options to finance their ADU, including savings, funds from family, and/or loans. It is strongly recommended that your financing is in place before construction starts. Be sure to factor in potential rental income since that will help you repay loans. See your County Guidebook and Exercises for more details on financing options.
What will it cost to build an ADU?
Your County ADU Calculator is a great place to start when developing a budget. It provides a rough estimate of costs and income and will help you understand how choices can impact your budget over time. In general, it is helpful to avoid having a fixed budget total in your head as you explore your options. The cost to build an ADU typically ranges from $30,000 for a simple interior conversion JADU, to $400,000+ for a large detached ADU with high-end finishes on a hillside lot. Cost per square foot is a good way to estimate, though this too can vary — a very rough placeholder for you to use is $300 range per square foot for construction (“hard costs”) and design and fees (“soft costs”), depending on your design and the materials you chose.
See more details about costs – including design, permitting, and construction – in your County Guidebook.
Will I need to add parking?
Parking is much less of a concern than it used to be. JADUs do not require a parking spot. Check County ADU Rules and talk with your staff to see if ADUs require additional parking. No new parking is required if ADU is: 1) within ½ mile walking distance to transit (including a ferry); 2) within an architecturally or historically significant district; 3) on-street parking permits are required and not provided to the occupant of the ADU; 4) located within one block of car-share access, or 5) built as part of a new home. Check the County ADU Rules to see what parking may be required.
Can I rent my ADU as an AirBnB or other short-term rental?
Generally, ADUs and JADUs cannot be rented for fewer than 30 days at a time.
Do I need to live in the main house to build an ADU or JADU?
Generally, homeowners are not required to live on their property if it includes an ADU. However, the County may require JADU owners to live in the primary unit or the JADU – and this may need to be recorded in a deed restriction for the property. To confirm owner occupancy rules for your area, check County ADU Rules and talk with staff early to find out.
I don’t think I can fit an ADU on my property – what can I do?
According to state law, rules about setbacks, lot coverage, and open space requirements cannot restrict you from building an 800 square foot ADU, as long as the ADU has setbacks of at least 4 feet and is not above 16 feet tall. Front setbacks also cannot restrict you from building an 800 square foot ADU, which means an ADU can be in a front yard – but only if rear or side placement isn’t possible.
How large can my ADU be?
According to state law, you can build up to an 800 square foot ADU, as long as it is not over 16 feet tall and rear and side setbacks are 4 feet or more. Otherwise, size limits depend on your property and local rules. No room behind or next to your main home? You can build it in your front yard instead.
How many ADUs and/or JADUs can I build?
Homeowners can build both an ADU and JADU on their property. Multifamily properties can have multiple ADUs, depending on the type and other details of the project. Contact staff for more information if interested in building ADUs on a multifamily property.
What zoning designations allow ADUs and JADUs?
ADUs and JADUs are allowed in all residential and mixed-use zones, with limited exceptions for safety, traffic, and water.
Can I put an ADU in my garage?
Homeowners can convert legally built structures (garage, barn, art studio, etc.) into an ADU. JADUs can be converted from an attached garage (but not detached). If you demolish your garage or other enclosed structure and build an ADU in its place, the ADU can be in the same footprint if it’s the same size and height of the structure it’s replacing. You may need to provide replacement parking; check County ADU Rules, see your County Guidebook, and talk with staff for more details.
If you plan on replacing a detached garage with an ADU, demolition permits, and public notice cannot be required if you have your ADU permit (unless it is in an architecturally and historically significant district). Check with staff for other garage-related policies.
Note that garage conversion ADUs may require significant moisture barriers and other design elements in order to meet building codes.
Am I allowed to build an ADU?
In almost all cases, yes! ADUs and JADUs are allowed in all single-family and mixed-use zones. If residential buildings are allowed, ADUs are almost always allowed too (with limited exceptions for safety, traffic, and water).
What do I need to do if I have a well?
ADUs may require a well report and well systems may need to be upgraded. Contact your County Environmental Health Department early in the process. For contact information, see the Contact page.
What do I need to do if I have a septic system?
ADUs often need separate waste treatment and your system may need to be modified. Contact your Environmental Health Department early in the process. For contact information, see the Contact page.
Do I need to tell my neighbors?
You’re not required to tell your neighbors about your ADU, but it’s always a good idea to communicate with them early in the process. Your project will run more smoothly if they are kept informed, and they may have great ideas for your project!
If you live in a Neighborhood or Homeowners Association, talk with your representative or board early in the process. They can’t prevent you from building or renting an ADU, but they may have guidelines you’ll need to know for design and construction. Depending on where you live, written approval from your HOA may be required before your location will permit your ADU.
How long does it take to build?
Building an ADU is an investment of time as well as money. Most projects take one to two years to complete. Typically, it takes homeowners one to three months to get started and assemble their team, then one to six months to develop plans, meet with the city, and submit the application. Depending on what permits are required, how many rounds of review are required and how quickly a homeowner and their project team can respond to comments, it will take one to six months to get permits. Construction usually takes six to twelve months.
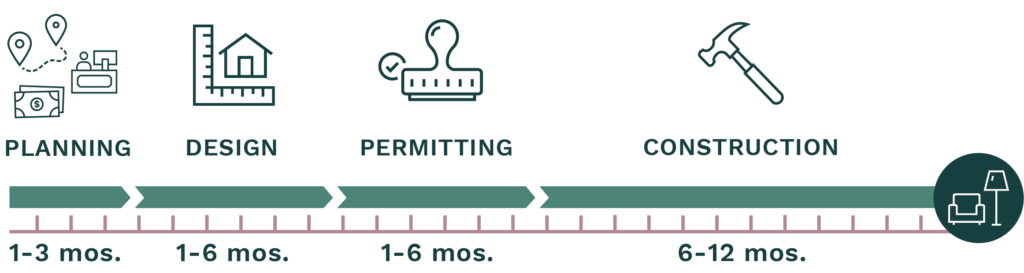
What do I have to do to build an ADU?
This site walks you through each part of the ADU process, from gathering initial inspiration and learning what you can build through construction and becoming a landlord or moving in.
You can also use our Process-At-A-Glance resource for an overview of the process and some initial issues to consider as you get started.
Start with Getting Started and walk through the pages of this site one-by-one for a detailed guide on what to do next.
What is the difference between a site-built and a prefabricated or manufactured ADU?
Site-built/Traditional: A traditionally constructed ADU is designed and built specifically to your preferences and property and built on site (“stick-built”). This option allows for a lot of customization and smaller changes to be made throughout the construction process.
Prefabricated/panelized/modular: These ADUs are partially or mostly built in a factory, then shipped to your site to be put together. Sometimes the company will include all services in their fee (“turn-key”), including help with permitting and all on-site construction tasks (e.g., laying the foundation, utility hookups, etc.). Other times you’ll need to hire additional professionals to help.
What is the difference between an ADU and a JADU?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) come in many shapes and sizes but are always a self-contained home that is usually smaller than the main house and legally part of the same property. They must have a kitchen, bathroom, and place to sleep, and typically range from studios under 500 square feet to over 1,000 square-foot homes with multiple bedrooms.
Junior Accessory Dwelling Units (JADUs) are within the footprint of your home (or attached garage) and less than 500 square feet. They can share a bathroom with the main home and/or have an efficiency kitchen (sink, cooking appliance, fridge, and small counter). Construction costs for JADUs are typically much lower. In most cases, the property owner must live on site in either the main home or the JADU.
State law now allows homeowners to have both a JADU and a regular ADU on their property.



